
DOWNLOAD A PDF OF THIS REPORT pdf(0.1MB)
Contact
Melissa BurekFounding Partner [email protected] 212-921-9354 Shaun Bisman
Principal [email protected] 212-921-9365
Highlights
- Companies continue to refine their existing stock ownership guidelines and stock retention requirements to demonstrate good governance and support shareholder alignment
- 98% of companies have one or both of these types of guidelines
- Median CEO stock ownership guideline has increased to 6x base salary from 5x since 2010
- Stock retention requirements have increased in prevalence since 2010, with 49% of companies using stand-alone stock retention requirements and/or stock retention requirements associated with a stock ownership guideline
Survey Sample
Compensation Advisory Partners (“CAP”) reviewed 2014 proxy disclosures at a sample of 100 companies among the Fortune 500, representing nine industry groups. Industry groups included: Automotive, Consumer Goods, Financial Services, Health Care, Insurance, Manufacturing, Pharmaceutical, Retail, and Technology. For the companies studied, the median revenue size and market capitalization was $32B and $52B, respectively. The median 2013 total shareholder return (TSR // change in stock price plus dividends) was 43%.
PREVALENCE OF STOCK OWNERSHIP GUIDELINES AND STOCK RETENTION REQUIREMENTS
The prevalence of stock ownership guidelines among companies reviewed is approximately 93%, showing a slight uptick since 2010, when approximately 89% of companies had stock ownership guidelines in place. Between 2010 and 2013, companies with both stock ownership guidelines and stock retention requirements increased to 44% from 22%, while the prevalence of having only stock retention requirements remained flat at 5%. The number of companies with no form of stock ownership guidelines or stock retention requirements decreased to 2% from 5%. Companies are demonstrating increased efforts toward good corporate governance by ensuring executives hold a meaningful amount of equity.
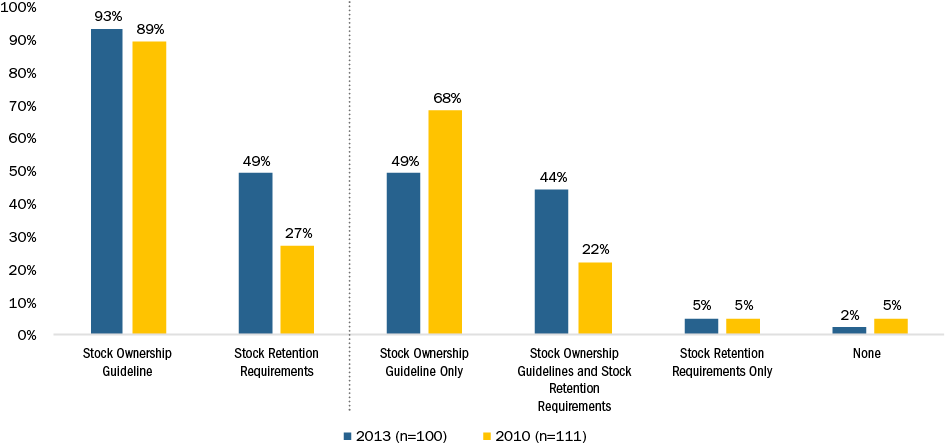
The most common stock retention requirement is to require executives to hold shares until a stock ownership guideline is achieved (34 companies). Implementation of stand-alone stock retention requirements that apply even after a stock ownership guideline has been achieved (25 companies) is a growing trend that we have seen over the last 3 years.
Prevalence of Different Forms of Stock Retention Requirements (n=49)
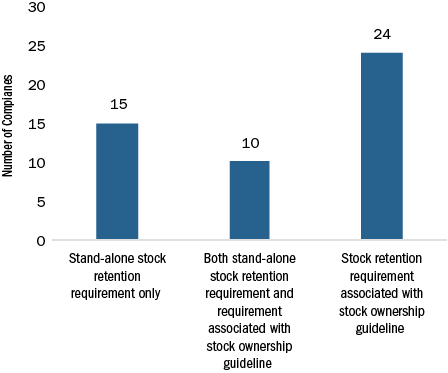
EXAMPLES OF STOCK RETENTION REQUIREMENTS
Stand-alone stock retention requirement only: AT&T
“Executive officers are required to hold 25% of the AT&T shares they receive (after taxes and exercise costs) from an incentive, equity, or option award granted to them after January 1, 2012, until one year after they leave the Company.”
Both stand-alone stock retention requirement and requirement associated with stock ownership guideline: Lincoln Financial Inc.
“If at any point the ownership guideline is not met with shares otherwise owned by the executive, the executive would be required to retain 50% of the net profit shares resulting from previously granted equity-based long-term incentive plan awards that are exercised or vest as applicable. Additionally, once an executive has met the minimum share ownership levels, they are also required to retain an amount equal to 25% of the net profit shares resulting from equity-based long-term incentive plan grants for five years from the date of exercise for stock options or the date of vesting for other awards.”
Stock retention requirement associated with stock ownership guideline: Gap, Inc.
“Executives not meeting the requirement must retain 50% of after-tax shares acquired through stock compensation programs until the requirement is reached.”
STOCK OWNERSHIP GUIDELINES
83% of companies express stock ownership guidelines as a multiple of salary and 13% express guidelines as a fixed number of shares. Fixed share guidelines tend to be more prevalent in the Financial Services (50%), Technology (33%), and Retail (33%) industries. Companies that use a fixed share approach generally have a volatile stock price, so locking in on a number of shares helps mitigate the potential challenges of meeting the stock ownership requirement.
|
CEO Stock Ownership Requirement Prevalence |
2013 (n = 93) |
2010 (n = 99) |
||
|
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
|
|
Multiple of Salary |
77 |
83% |
80 |
81% |
|
Fixed Shares |
12 |
13% |
15 |
15% |
|
Lesser Of Approach |
1 |
1% |
2 |
2% |
|
Other* |
3 |
3% |
2 |
2% |
*Other includes: Fixed Value, Multiple of Target Cash and Multiple of Notional Base
Stock ownership guidelines for CEOs have increased since 2010, with the median requirement increasing from 5x to 6x multiple of salary in 2013. The median fixed share guideline also increased to 250,000 shares compared with 150,000 shares in 2010. This suggests that companies may be increasing their fixed share guidelines to align with companies that have adopted higher multiples of salary. In 2013, the median stock ownership requirement value for the CEO is $7.7M compared with $6.7M in 2010, a significant increase of approximately 15%.
|
CEO Stock Ownership Requirement |
2013 (n = 100) |
2010 (n=99) |
||||
|
25th %ile |
50th %ile |
75th %ile |
25th %ile |
50th %ile |
75th %ile |
|
|
Multiple of Salary |
5x |
6x |
7x |
5x |
5x |
6x |
|
Fixed Shares |
125,000 |
250,000 |
500,000 |
100,000 |
150,000 |
300,000 |
|
Total Value |
$6.3M |
$7.7M |
$9.7M |
$5.4M |
$6.7M |
$8.6M |
Most companies require executives to achieve an ownership guideline requirement within 5 years. Thirteen companies (14%) disclosed a penalty for not achieving the required ownership level. The most common penalties for non-compliance include restrictions on selling shares (75% of companies), followed by reductions in future total compensation (25% of companies).
When determining which shares count towards ownership requirements, companies must consider whether to include unvested full-value shares, unexercised options or unearned performance shares. Of the companies reviewed, 69 out of 93 disclose the type of shares that count toward the guideline. Approximately 40% of companies count unvested restricted stock toward the requirement, (up from 33% in 2010) and less than 10% count unvested options or vested but unexercised options.
|
Shares Counting Toward Guideline Requirement |
2013 (n = 93) |
2010 (n = 99) |
||
|
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
|
|
Shares directly owned |
65 |
70% |
55 |
56% |
|
Shares in 401(k) plan |
37 |
40% |
33 |
33% |
|
Unvested restricted stock |
36 |
39% |
33 |
33% |
|
Shares indirectly owned |
32 |
34% |
29 |
29% |
|
Deferred compensation |
26 |
28% |
25 |
25% |
|
Vested but unexercised options |
7 |
8% |
6 |
6% |
|
Unvested options |
1 |
1% |
1 |
1% |
|
Not disclosed |
24 |
26% |
29 |
29% |
Note: Percentages add up to greater than 100% due to multiple types of equity counted by various companies.
Companies generally do not count unearned performance shares toward stock ownership guidelines. It is more common to included unvested restricted stock, as the eventual vesting of these shares is much more certain, since achievement of performance hurdles is not guaranteed.
STAND-ALONE STOCK RETENTION REQUIREMENTS
Companies with stock retention requirements most often require executives to hold net shares from option exercises, restricted stock share/unit vesting or performance share payouts. Requiring executives to hold net shares for one year post exercise or vest (64%) has remained the most prevalent holding period, increasing from 46% prevalence in 2010. Other companies require executives to hold shares for a 1 year period post-retirement (20%), while fewer companies require shares to be held until retirement (8%).
|
Period Subject |
2013 (n = 25) |
2010 (n = 24) |
||
|
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
|
|
1 year post exercise/vest |
16 |
64% |
11 |
46% |
|
2 years post exercise/vest |
0 |
0% |
1 |
4% |
|
Retirement |
2 |
8% |
8 |
33% |
|
Post-retirement |
5 |
20% |
1 |
4% |
|
Other |
2 |
8% |
4 |
17% |
|
Not disclosed |
0 |
0% |
1 |
4% |
Note: Holding requirement only for companies with stand-alone holding requirement. Percentages may add up to greater than 100% due to different holding periods for the CEO vs. other NEOs.
STOCK RETENTION SHAREHOLDER PROPOSALS
While companies may maintain stock ownership guidelines and/or stock retention requirements, they are not shielded from receiving shareholder proposals that require executives to hold a meaningful percentage of equity until requirement. Among the Russell 3000, 30 companies in 2014 and 46 companies in 2013 received shareholder stock retention proposals. In all cases, the proposals failed or were withdrawn. The median level of shareholder support for these proposals was less than 25%.
Disclosed Changes to Stock Ownership Guidelines and Stock Retention Requirements
22% of companies disclosed making a recent change to their stock ownership guidelines. Of those companies that modified their guidelines, the two most common changes were adopting a stock holding requirement (32%) and increasing the ownership guideline (27%).
|
Changes To Stock Ownership Guidelines and Stock Retention Requirements |
2013 (n = 22) |
2010 (n = 25) |
||
|
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
# of Cos |
% of Cos |
|
|
Added holding requirement |
7 |
32% |
6 |
24% |
|
Increased guideline requirement |
6 |
27% |
12 |
48% |
|
Newly adopted stock ownership guideline |
5 |
22% |
1 |
4% |
|
Changed fixed value / multiple approach |
2 |
9% |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Adopted mandatory holding of shares through retirement |
1 |
5% |
1 |
4% |
|
Extended participation |
1 |
5% |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Modified penalty for non-compliance |
n/a |
n/a |
5 |
20% |
SUMMARY
In 2014, companies continued to practice good governance by enhancing their stock ownership guidelines. Additionally, companies continue to implement stock retention requirements, albeit at a slower rate. Stock retention requirements most often serve as a supplement to existing stock ownership guidelines. Overall, we expect companies to continue to strengthen their stock ownership and stock retention requirements because these policies address issues important to both shareholders and proxy advisory groups, and align executives with shareholders.









